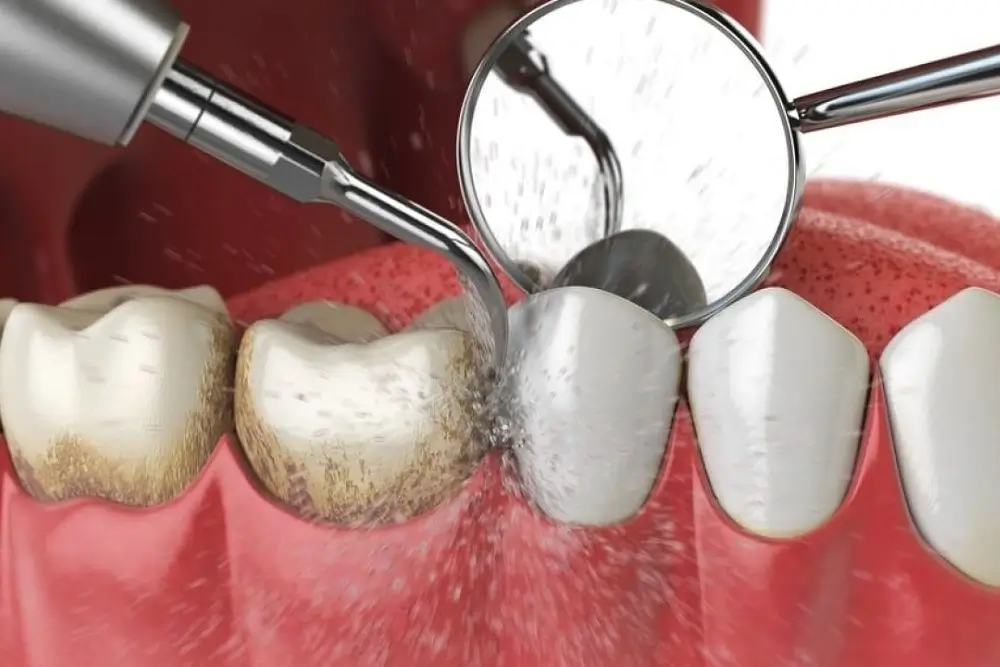
Calculus (or tartar) is a hard substance created by mineralized plaque on the surfaces of the tooth. If not removed, plaque will turn into calculus after around 2 weeks.
It is predominantly made up of calcium phosphate and survives well in the burial environment. There are two forms of calculus: supra- and subgingival, describing its location on the crown or root of the tooth, respectively.